How to Evaluate an LLM: Benchmarks, Metrics, and Practical Workflows
Evaluate your LLM using MMLU, MT-Bench, LLM-as-judge, and ROUGE. Covers lm-evaluation-harness, fine-tuned model comparison, and evaluation pitfalls. With code.
Evaluate your LLM using MMLU, MT-Bench, LLM-as-judge, and ROUGE. Covers lm-evaluation-harness, fine-tuned model comparison, and evaluation pitfalls. With code.
Fine-tune LLMs with Unsloth — 2x faster training, 70% less GPU memory. Step-by-step guide with LoRA, QLoRA, code examples, and deployment tips.
Learn LLM evaluation from scratch -- benchmarks, metrics (BLEU, ROUGE, perplexity), LLM-as-judge, and custom pipelines with runnable Python code.
Fine-tune LLMs with LoRA and QLoRA in Python. Complete guide covering memory math, PEFT setup, 4-bit QLoRA, adapter merging, and common mistakes — with...
Align LLMs with human preferences using one loss function -- no reward model, no RL. Complete guide with derivation, PyTorch code, and DPO variants.
Learn how to build a custom instruction dataset for LLM fine-tuning — covering Alpaca, ShareGPT, and DPO formats, quality filtering, synthetic data generation, token...
Learn how to fine-tune large language models with LoRA in Python using PEFT and TRL — covers LoraConfig, QLoRA, SFTTrainer, model merging, and common...
Learn how LLMs work from tokenization to text generation. Build self-attention from scratch in Python with verified code and 3 interactive exercises.
Learn how to build a Python AI chatbot with memory using the OpenAI API. Covers conversation history, token management, streaming, and a complete reusable...
Build your first AI app with Python and the OpenAI API. Step-by-step tutorial covering chat completions, streaming, error handling, and cost control — with...
 11 min
11 min
Creating custom regressors in scikit-learn means building your own machine learning models that follow scikit-learn’s API conventions, allowing them to work seamlessly with pipelines,...
If you’ve ever read a scientific study, survey results, or even a political poll, you’ve probably encountered confidence intervals (CIs). They’re one of the...
 14 min
14 min
Optimal chunk size for RAG systems typically ranges from 128-512 tokens, with smaller chunks (128-256 tokens) excelling at precise fact-based queries while larger chunks...
This is one of the most beautiful connections in machine learning – let me break down exactly why Ridge regression is MAP estimation in...
 14 min
14 min
Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) estimation is a Bayesian method for finding the most likely parameter values given observed data and prior knowledge. Unlike maximum...
 28 min
28 min
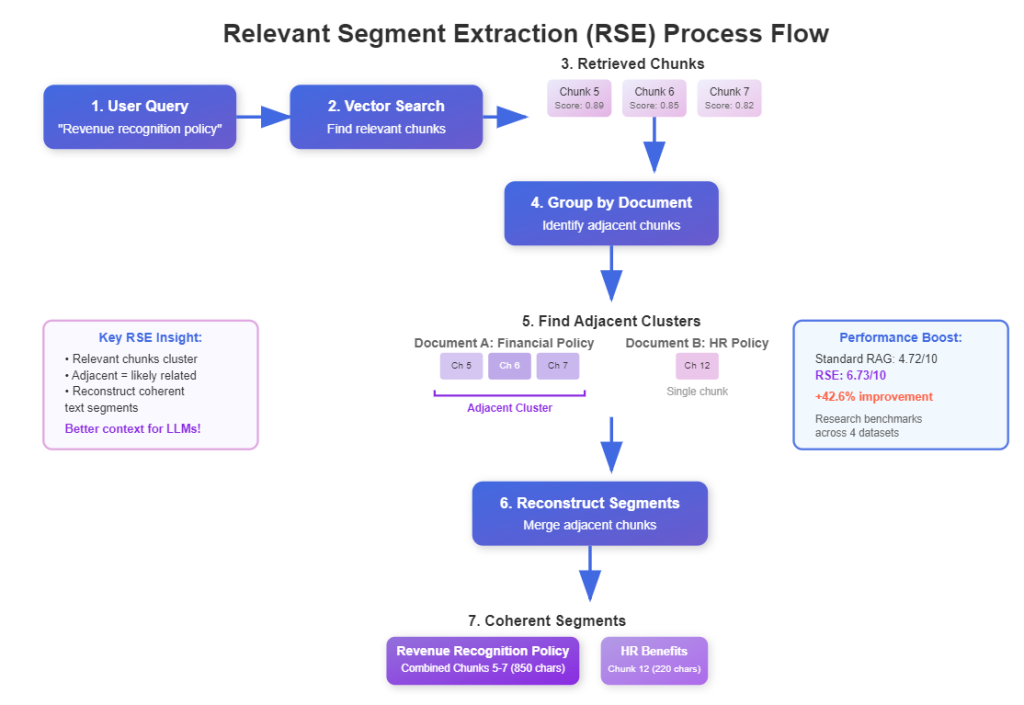
Relevant Segment Extraction (RSE) is a query-time post-processing technique that intelligently combines related text chunks into longer, coherent segments, providing LLMs with better context...
Ollama is a tool used to run the open-weights large language models locally. It’s quick to install, pull the LLM models and start prompting...
While GPUs ((Graphics Processing Unit) are in high demand in video games, with the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs), GPUs are in high...
Cross-entropy is a measure of error, while mutual information measures the shared information between two variable. Both concepts used in information theory, but they...
The F statistic is used in statistical hypothesis testing to determine if there are significant differences between group means. It is most commonly used...
Get the exact 10-course programming foundation that Data Science professionals use.